Power Supply
Less than 50%of households have access to electricity for more than 12 hours
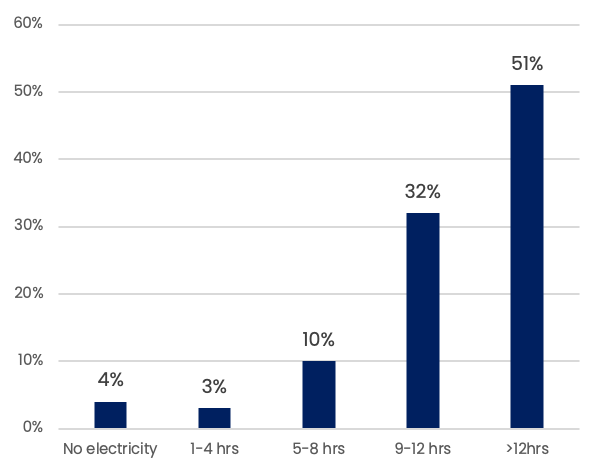
Source: Ministry of Rural Development, Mission Antyodaya, 2019
Power Cuts
Metros get seven hour s more power on average than under-developed rural areas
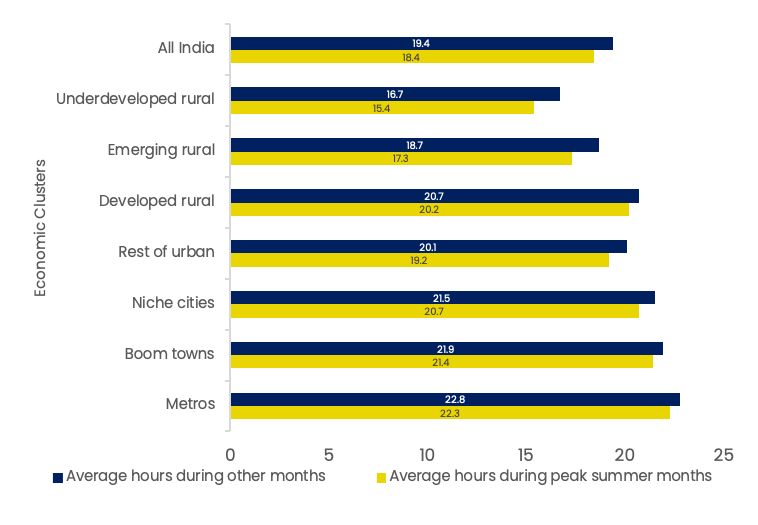
Source: ICE 360Survey, 2016, from People Research on India's Consumer Economy (PRICE)
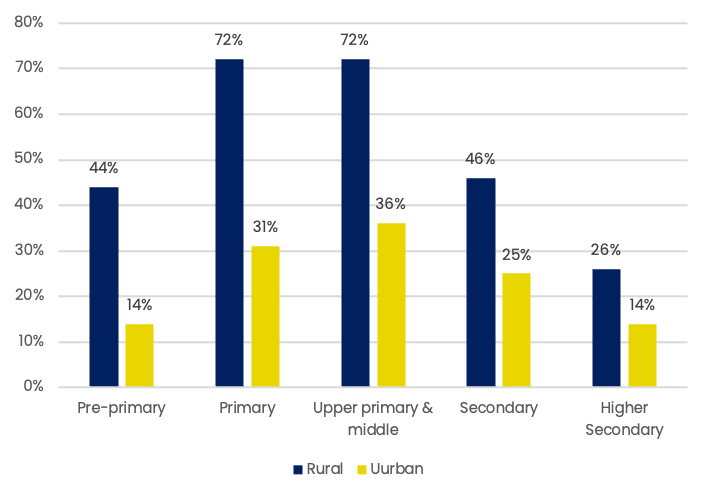
Households with access to computers (%)
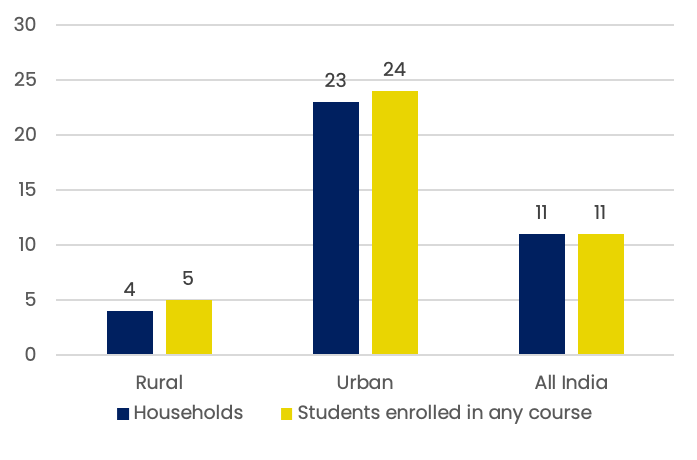
Source: NSS 75th Round, 2019
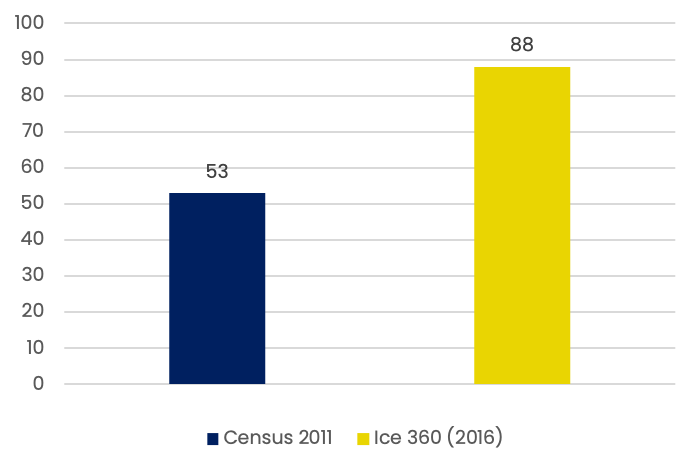
Households with mobile phone (%)

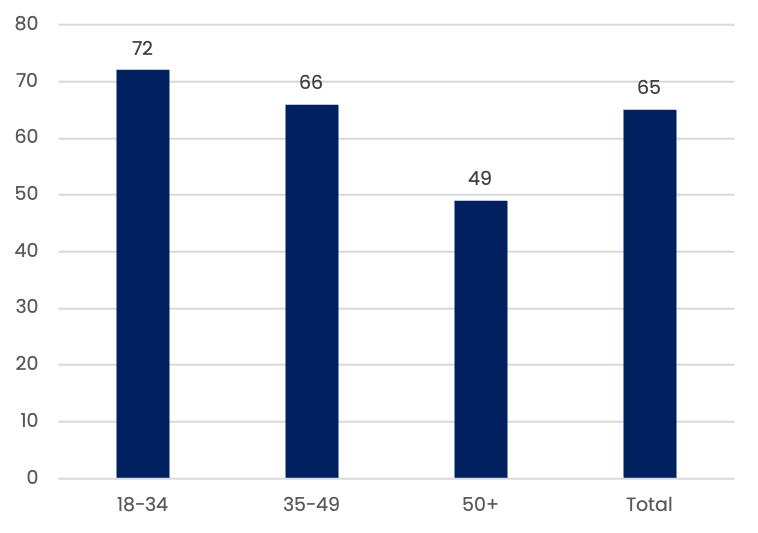
Mobile phone ownership by age-group (%)
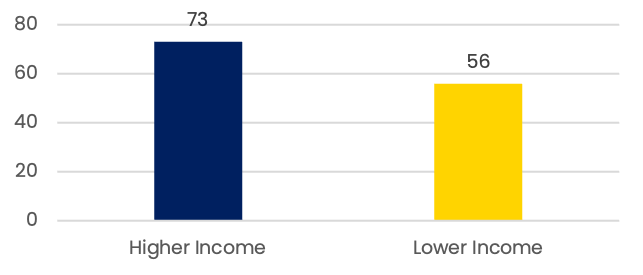
Mobile phone ownership by income group (%)
Mobile phone ownership by gender(%)
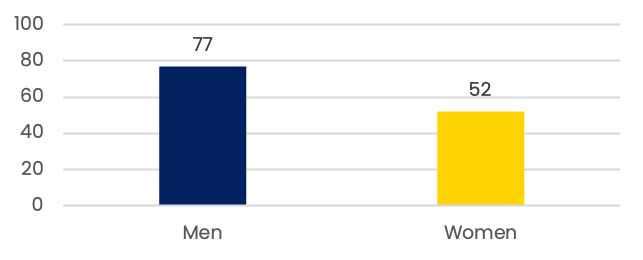
Internet subscribers in India (mn)
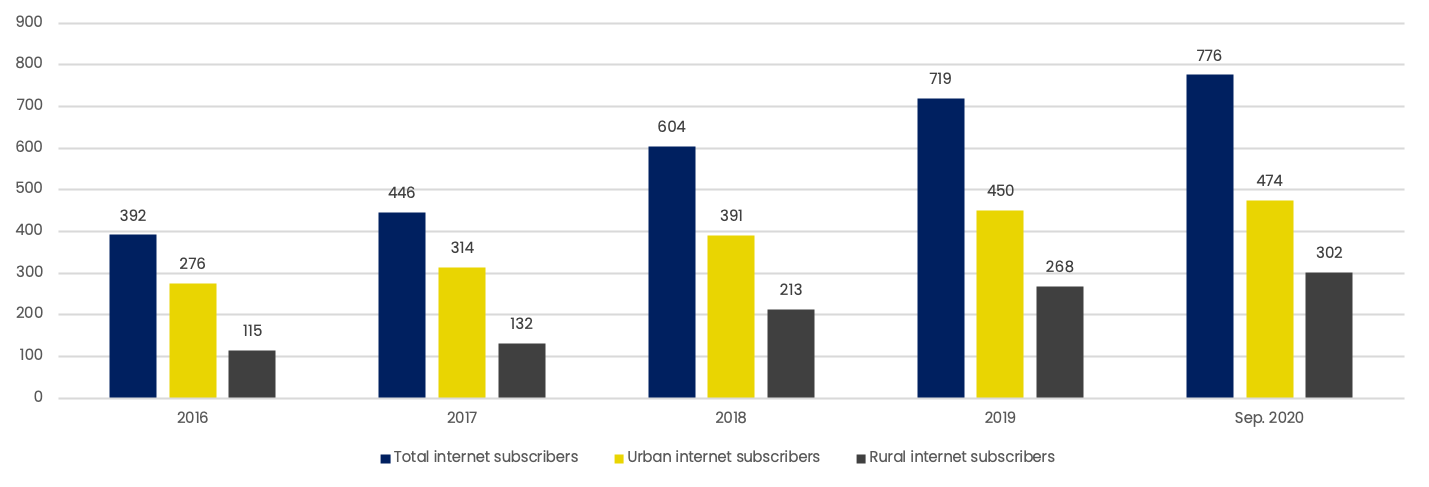
According to TRAI, as ofSeptember 2020, 96.78% of all internet subscribers in India were mobile wireless subscribers
Rural-urban gap in internet access
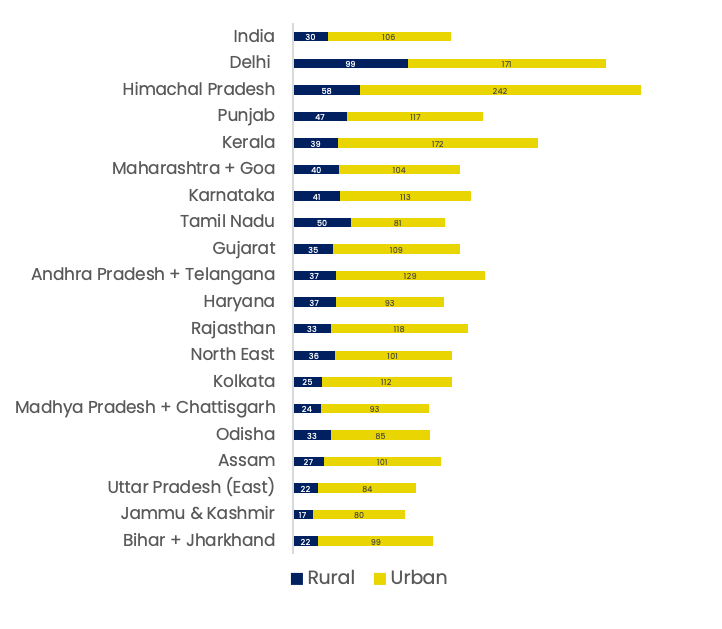
Source: TRAI (as on December 2019)
Note: Data not given for three circles – Mumbai, Uttar Pradesh (West) and West Bengal(including Sikkim)
Internet usage by gender (%)
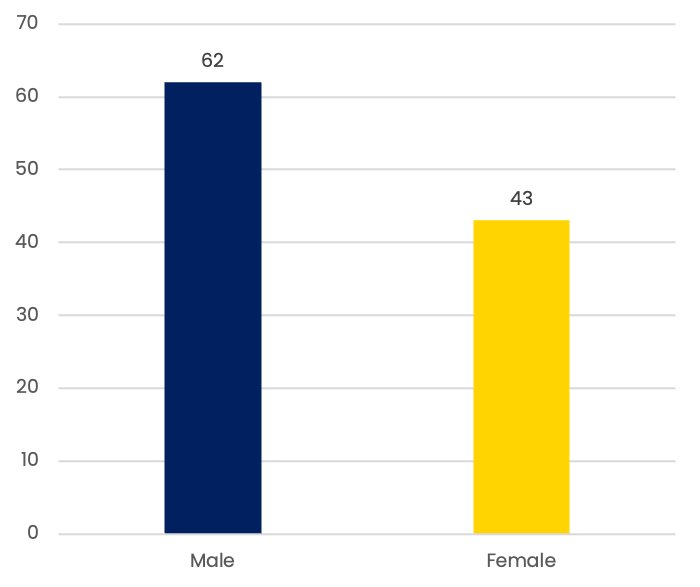
Source: National Family Health Survey 5, 2019-20
ICE 360 Survey, 2016
2016
1. Access to internet at home2. Access to internet
(not restricted to home)
61,000 households
- 10% (27 million) householdsreported having
internet connection at their home
- 22% (62 million) of Indian households have at least one member accessing the internet (either at work orhome or elsewhere, and either through a computer or mobile)
NSSO75th Round
2017-2018
Access to the internet is defined as a household possessing any device, such as computer, tablet, smartphone, etc, through which internet facility is available, whether or not it has been used
1,13,757 households
- 24% have internet facility
- 15% in rural, 42% in urban areas
NFHS-5
2019-2020
Men/ Women who have ever
used the internet
610,000 households
42.6% of women ever used theInternet as against
62.16% of men
Urban : 56.81% women in urban India ever used the Internet compared to 73.76 % among the men
Rural : 33.94 % women in rural India ever used the Internet as against 55.6 % among men
ICUBE Digital Adoption and Usage Trends
2020
Active internet users
75,000 households
574 million active internet user
For a large segment of India’s population a smartphone could still cost 3-16% of their daily income(GSMA-Dalberg, 2017)
<$2
19.80%
16%
9%
$2-10
76.90%
3-16%
1-5%
$10-20
2.60%
2-3%
0.5-1%
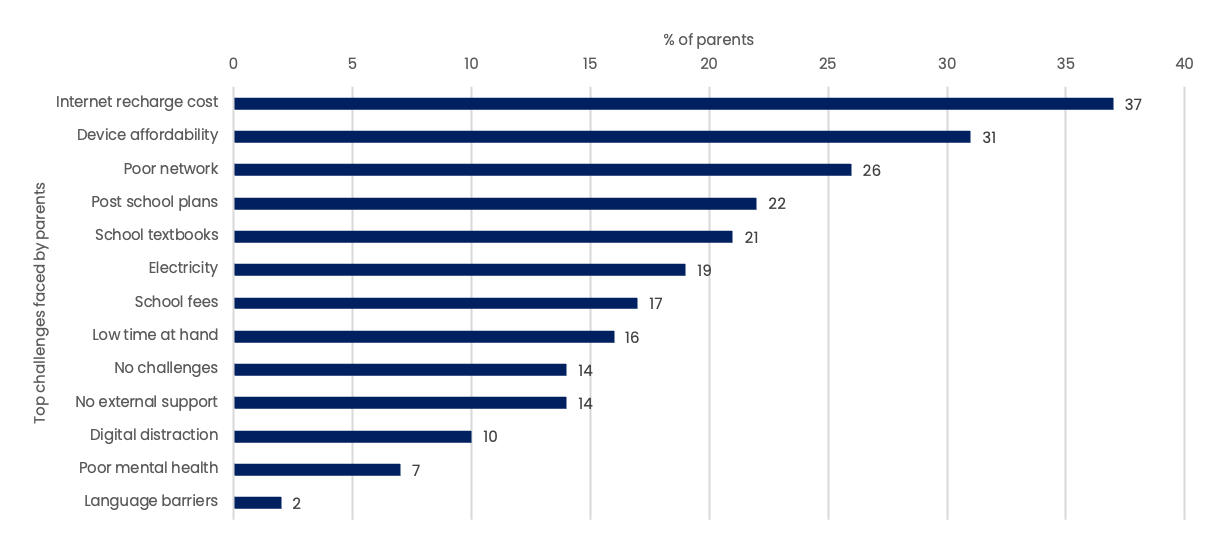
According to a recent UNICEF study, parents report that data costs (37%), device affordability (31%), and poor network connectivity (27%) as key constraints to remote learning for their children

Do children have a smartphone at home?
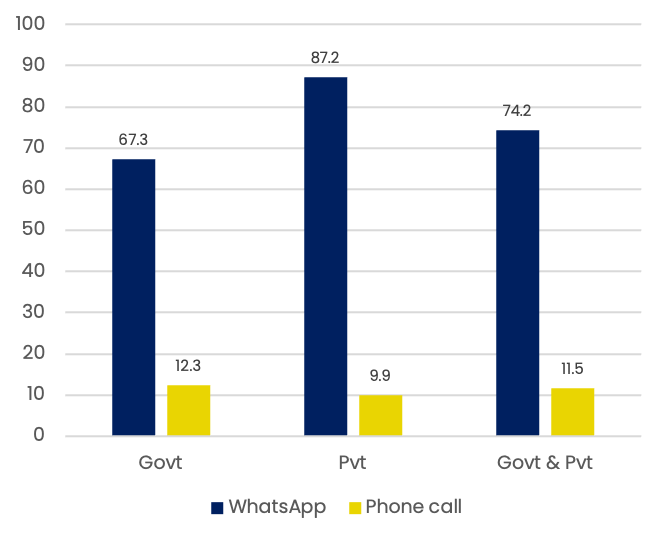
Phone based mediums of sharing learning content
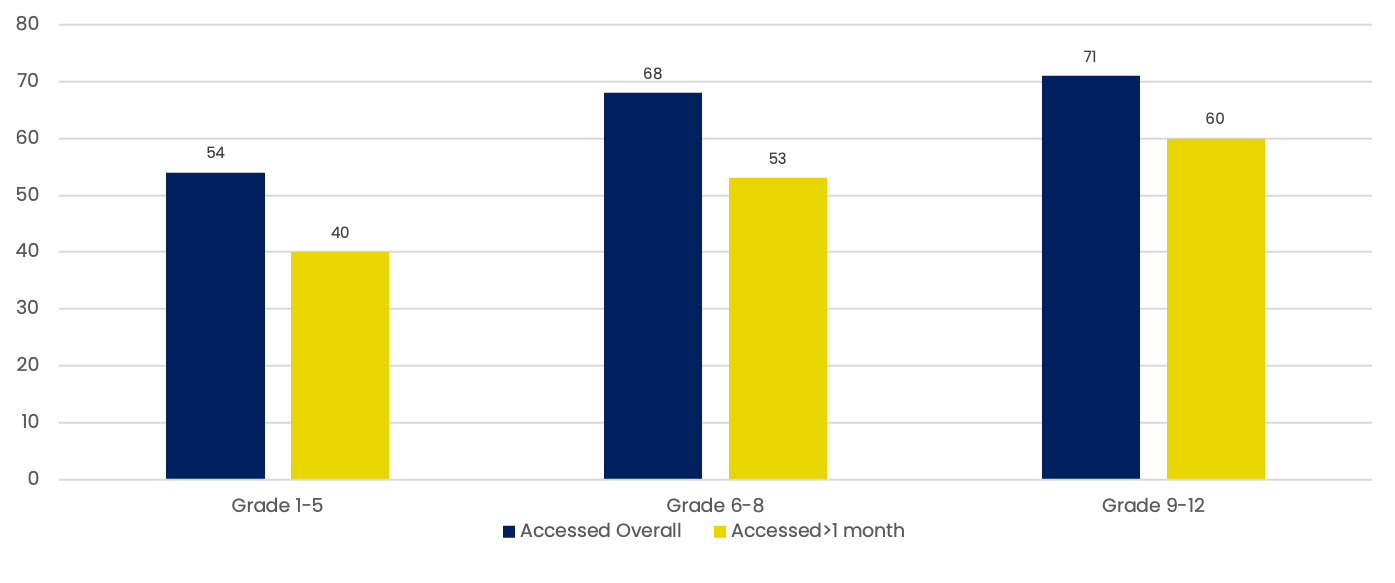
Accessing learning content by grade (% of children between 5-13 & 14-18 years of age)
% of children who receive from family members while studying at home
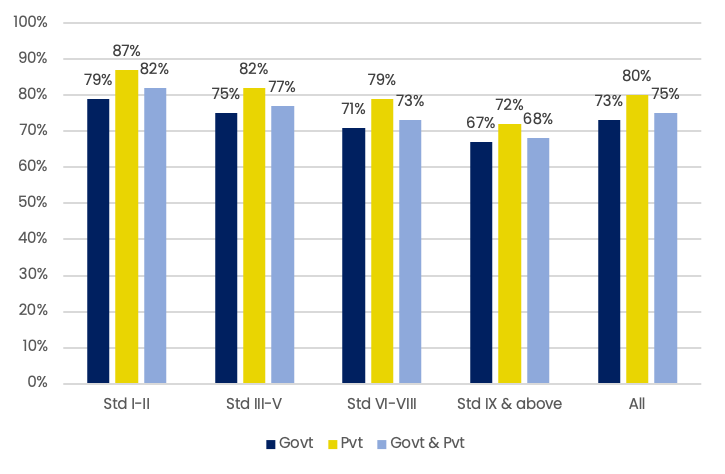
During school closures, children relied on getting help from family members for at-home learning
% of enrolled children who receive family support for learning - by parent education
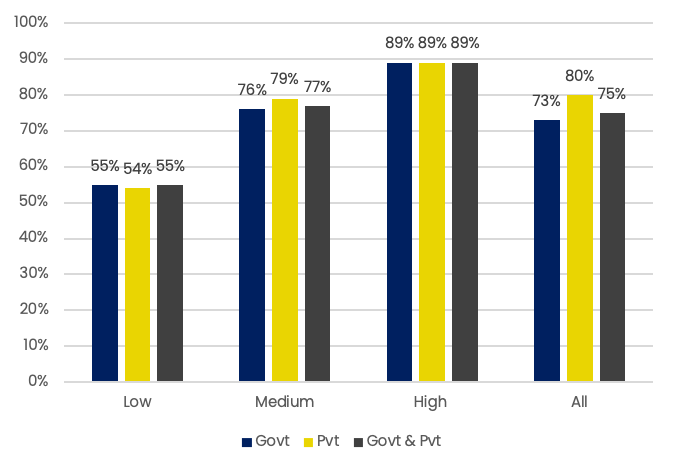
Parents with greater level of education provided more support to children for at-home learning

Education levels
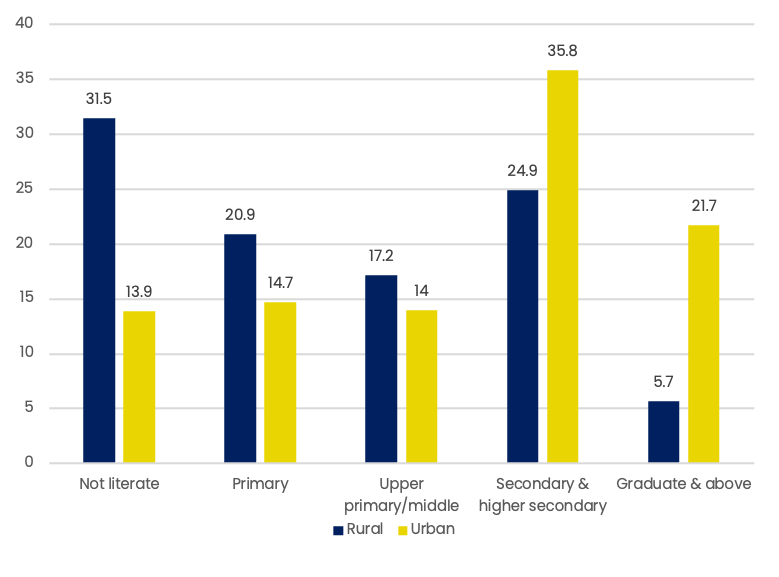
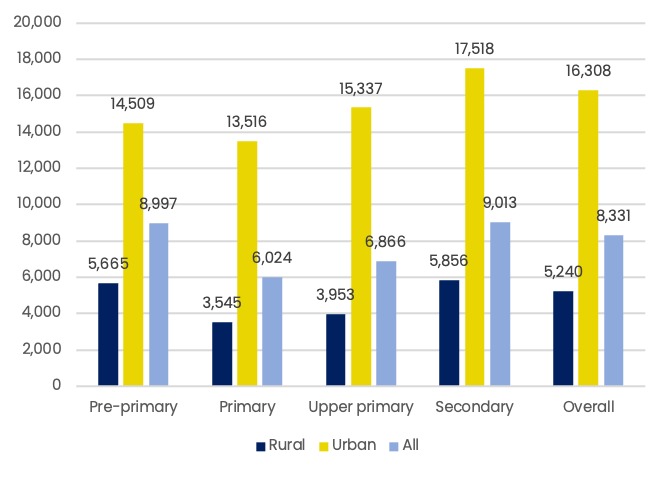
Household spending on education per student for all grades
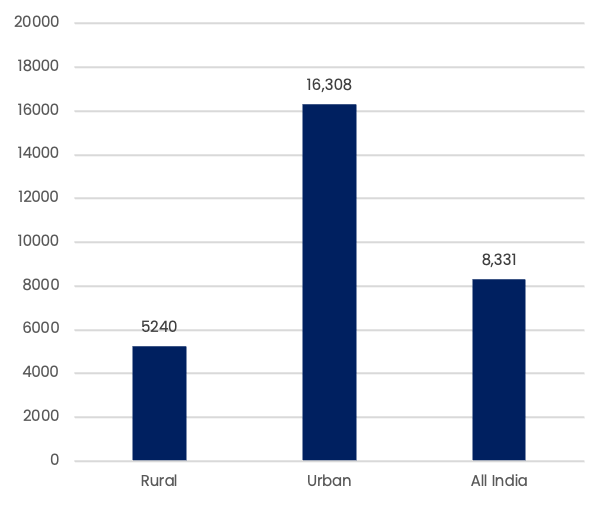
Household spending on education per student
Proportion of students accessing free education (NSS 75th Round)