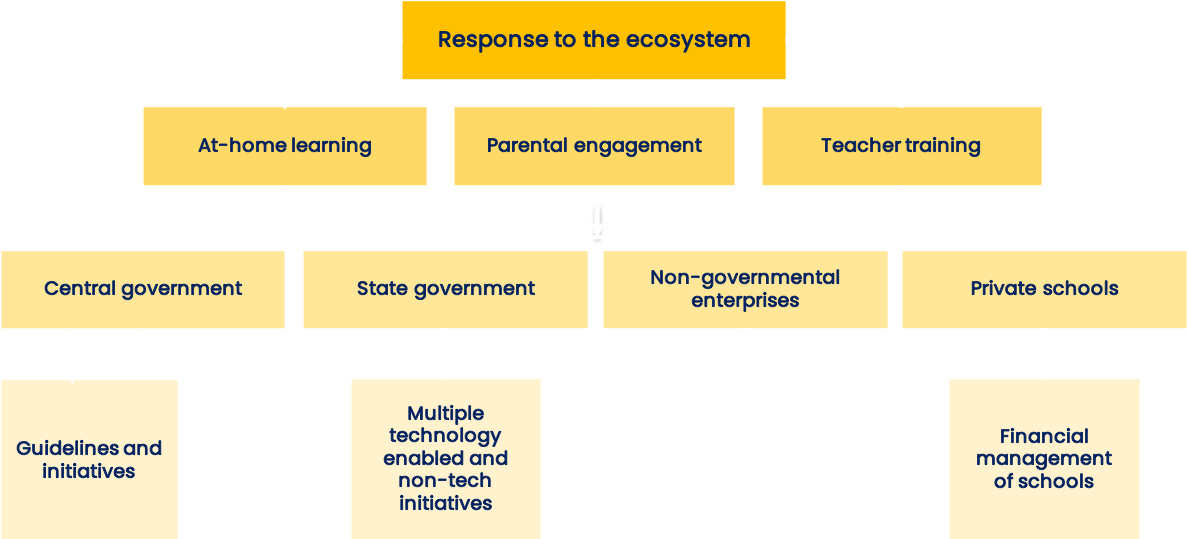
Pragyata guidelines
(MHRD, 2020)
Learning enhancement guidelines
(NCERT, 2020)
Alternative academic calendar (AAC)
(NCERT, 2020)
Launch date
July 2020
August 2020
September 2020
Content
Eight steps for digital and online education, i.e.
Plan, Review, Arrange, Guide,
Yak (talk), Assign, Track,Appreciate
Continuous learning plans, models of learning enhancement for students without or with limited access to digital devices, roles of various stakeholders and how these will change in the post pandemic world
Under PM-e-Vidya, week-wise plans with curriculum related activities and challenges that teachers and parents can
opt for
Stakeholders
Students, state officials, school heads, parents and teachers
School heads, state officials, parents and teachers
Students, parents and teachers
MoE launched SWAYAM PRABHA TV channels to telecast educational content
for grades 1-12
Used 289 community radio stations and CBSE’s Shiksha Vani podcast to deliver content for grades 9-12 and 1-12, respectively
Several kinds of home learning e-content were made available on online repositories, such as NROER (NationalRepository of Open Educational Resources), DIKSHA and NCERT’s YouTube channel
The response was primarily in areas of providing e-content for teachers on online platforms, and conducting trainings online. These trainings aimed to continue teacher professional development that was disrupted by the pandemic, with a renewed focus on training for facilitation of remote learning.
The MoE trained about 30 lakh elementary school teachers digitally during 2020-21 and plans to train around 56 lakh teachers across the country in 2021-22 (Indian Express, February 13,2021)
Home Stations: 420 stations; reaching nearly 92% of India and 99.19% of total population in 23 languages (EY, 2019)
Households with TV: 210 million (BARC, 2021); with 80%penetration rate of paid cable and satellite TV (Statista, 2020)
Urban Telephone Subscribers: 647.36 million, Rural Telephone Subscribers: 524.44 million
88% of Indian households have a mobile phone(TRAI, 2020) (ice360, 2016)
Internet: Overall: 40% | Urban India: 54% | RuralIndia: 32%
433 million (12+ years) and 71 million (5-11 years; on family devices) (IAMAI, 2019)
Broadband Subscribers: 734 million (TRAI, 2021)11% of Indian households have access to a computer device(TRAI, 2020) (NSSO, 2019)
Textbooks distributed among 86.8%children/ parents (~96, 000 children) in rural India (ASER, 2021)
Mobile apps
Web-based portals
IVRS
TV
Radio
Print/offline
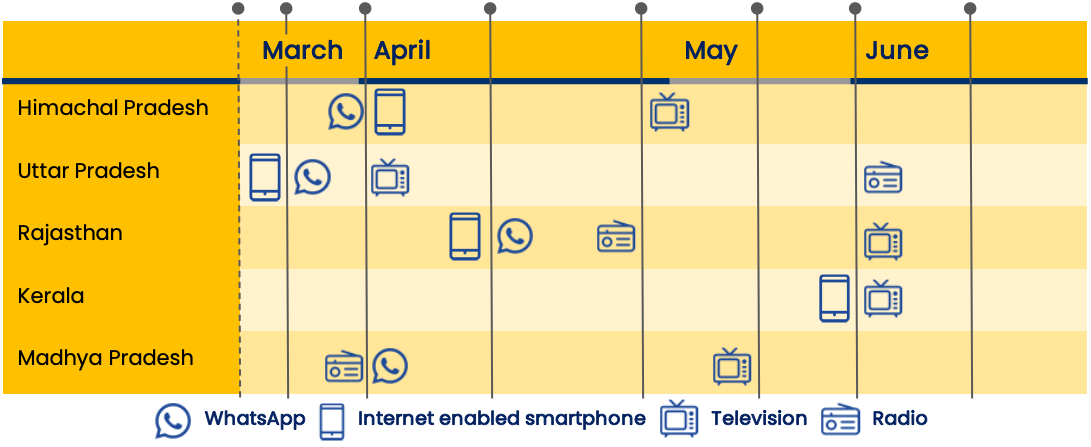
HP, JH, MP, RJ
CHT, HP, HR, KR, MP, RJ, TN, UP
CHT, HP, HR, JH, MP,RJ, TN, UP
CHT, HR, MP
HP, HR JH, KR, MP, RJ, TN, UP
HP, MP, RJ, UP
CHT, HP JH, MP
HP, MP
HP
MP
HR, KR, MP
JH
HP
CHT
MP, RJ
CHT, RJ
State abbreviations
CHT: Chhattisgarh
HP: Himachal Pradesh
HR: Haryana
JH: Jharkhand
KR: Kerala
MP: Madhya Pradesh
RJ: Rajasthan
TN: Tamil Nadu
UP: UttarPradesh
* The coverage of state responses is not exhaustive but limited to those states for which we were able to collect extensive and verified information
WhatsApp deployed across states
Gujarat
Study from Home
3,200 school groups, 35L+ students
Haryana
Ghar se Padhao
200+ school groups, 10L (50%)students
Jharkhand
Learning by WhatsApp
30,000 school groups, 10L students
Madhya Pradesh
DigiLEP
50,000+ school groups, 19L parents
Rajasthan
Project SMILE
9,226 school groups, 12.78L households
Uttar Pradesh
Mission Prerna
~1.4L school groups, 25L students
Source: MHRD, 2020, India Report Digital Education
Most states used WhatsApp to launch initiatives and cover a range of objectives, such as content delivery, assessments, monitoring and feedback, and doubt resolution
Rajasthan: Aao Ghar mein Seekhein, Project SMILE
Chhattisgarh: Har Ghar School
Haryana: Ghar se Padhao
Himachal Pradesh: Har Ghar Pathshala
States launched platforms or apps easily used by students to synchronously and asynchronously access content, ask questions and resolve doubts
DIKSHA , ConveGenius, Top Parent,Digi App, Learnytic, Sampark Didi, Shala Samvad, Gyan Pitara
Several states utilized existing reach and dissemination lines of TV and radio to broadcast educational content
Madhya Pradesh: DD, AIR
Tamil Nadu: KalviTholaikatchi
Kerala: VICTERS
Haryana: EDUSAT
Uttar Pradesh: English Seekho on AIR, DD
Radio
TV
Shikshavani: content broadcasted at 11am daily
Channel: DD Rajasthan
SMS/ IVRS/ Mobile phones
Audio bridge classrooms: Students used feature phones and landlines to connect to teachers without digital devices
Mobile apps
Bright Tutee
Use: Provides digital learning content Target group: Grades 9- 10
(Bweducation,April 2020)
Use: Partnered with ConveGenius, which uses AI-based WhatsApp chatbots to offer personalized assessments, doubt learning services and content recommendations to students (Bweducation, October2020)
Use:Teachers provided material to children and resolved doubts with Aao Ghar mein Seekhein & Project SMILE initiatives.Video content was also available on YouTube & DIKSHA (Dainik Bhaskar, 2020)(ETGovernment, 2020, 15)
Use: Delivered content and engaged parents with Har Ghar School campaign
Web-based portals
DIKSHA Content: 2,500+ topics from 28 books
Target group: Grades1-10
Shala Samvad (Rajshaladarpan, 2020)
Use: Other than e-learning content, special “talk to talk” interface allowed students to ask questions on the content, which were answered by a panel of experts.
E-platform under Padhaai Tunhar Duvaar (Cgschool, 2020)
Use: Provides children with content, such as live classes, offline video lectures, worksheets and podcasts.
Raise hand (ask question) section of platform
Use: Allows students to post questions, which are answered within 24-48 hours
Gamefied assessment solutions of platform
Use: Questions tagged to NCERT learning outcomes & rendered into small games (eg: online cricket) (Expresscomputer, May 2020)
Printed books/ offline learning
Loudspeaker schools: Teachers collaborated with local community/ panchayat for loudspeakers to relay audio lessons in remote areas
Radio
Radio School: Launched in collaboration with AIR
Content: Stories and academic content broadcasted daily for 1 hour in the mornings and evenings
Target group: Grades 1-8
TV
Channel: Kalvi Tholaikatchi
Content: Educational content broadcasted daily with fixed timetable (also available online with YouTube content)
Target group: Grades 2-12
Channel: DD MP
Content: Special educational programme,‘Classroom’ aired twice a day, 5 days a week
Target groups: Grades9-12
SMS/ IVRS/ Mobile phones
‘Humara Ghar Humara Vidyalaya’ campaign:Teachers visit student homes or phone them to track progress
Mobile apps
Use: Teachers used groups to send content and assignments to students and resolve doubts
Use: Partnered with ConveGenius, which uses AI-based WhatsApp chatbots to offer personalized assessments, doubt learning services and content recommendations to students (India education diary, 2020)
TopParent
Use: Delivers content & allows parents to track child’s progress through continuous report cards
Use: Delivery, curation, and monitoring of content under DigiLEP scheme
Web-based portals
Tamil Nadu e-learn Platform
Content: 10,000+ e-Learning content, 390 digital textbooks & 2,000+ aggregated YouTube videos
TNDIKSHA
Content: Energized textbooks that can be accessed via QR codes, 14,000+resources
Target group: Grades1-12
Gyan Pitara
Content: Online textbooks & videos
Target group: Grades3-8
In collaboration with Room to Read, digitized flip books with stories were sent to students every Sunday to inculcate the habit of reading (Times of India, 2020)
Printed books/ offline learning
Teachers distributed hard copies of weekly learning planners defining learning outcomes for students each day, based on their assessments and workbooks/ textbooks
Radio
Content broadcast via AIR stations in the state
TV
Channel: DD Himachal
Target group: Grades1-10
Channel: DD Jharkhand
Content: Lessons streamed for 4 hours everyday under
Hamara DoorDarshan Hamara Vidyalaya
Target group: Grades1-12
SMS/ IVRS/ Mobile phones
Mobile apps
Sampark Didi
Use: Virtual classes
and animated lectures at home
Target group:
Grades1-8
(ETGovernment,April 22, 2020) (BusinessLine,April 16, 2020)
Use -partnered with ConveGenius, which uses AI based WhatsApp chatbots to offer personalized assessments, doubt learning services, and content recommendations to students(TheLogical Indian, 2021)
Use: Used under ‘Har Ghar Pathshala to deliver content to and evaluate students through worksheets
Use: Delivered content for students and teachers as per structured calendar under digiSATH
DigiApp
Use: Developed by Jharkhand Education Project Council to deliver content to students
Target group: Grades1-8
(Prabhat Khabar, 2020)
Learnytic
Use: Developed by Jharkhand Education Project Council to deliver content to students
Target group: Grades9-12
(Prabhat Khabar, 2020)
Web-based portals
Samarth
assessment dashboard
Use: Managed & assessed learning profiles of students
Platform:
Official website of the state
Use: Hosts e-content including videos related to curriculum and worksheets for students
Printed books/ offline learning
In certain remote areas (such as Kaza), text books and hard copies of worksheets were circulated among students
Mohala schools: For students without digital access, teachers in green zones initiated classes for8-10 students with social distancing norms
Teachers go door to door to engage with students, get their feedback, and spread awareness about government initiatives
Radio
AIRand other channels used to broadcast audio-based learning programmes. English Seekho programmes were aired in partnership with UNICEF
TV
Channel: EDUSAT TV channels
Target group: Grades1-12
Channel: VICTERS educational channel
Targetgroup: Anganwadi to 12
Channel:Doordarshan UP
SMS/ IVRS/ Mobile phones
Ghar se Padhao Abhiyaan: Content sent via SMS
Teachers review student work via follow up calls and messages: 1,800 mentors call 15 parents each for feedback every week
Teachers used phones to collect feedback from parents and resolve doubts of students.Authorities are informed of the feedback, based on which suitable solutions are developed.
Content broadcast via AIR stations in the state
Mobile apps
Use: Under the Ghar se Padhao WhatsApp campaign, class groups were used to share content, daily activities, homework, and keep track of student performances (HindustanTimes, 2020)
Use: As part of Mission Prerna kie-Pathshala, teacher-to-student WhatsApp groups exchanged content.
Web-based portals
Platform:
Gharse Padhao website
Use: Hosts a variety of links to several kinds of home learning content
Platform:
Samagra
Use: KITE* created an online learning platform, which is a repository of academic and edutainment content. Content is also made available on YouTube and Facebook
Targetgroup: Grades1-12
Platform:
Website of Department of Education
Use: hosts several e-resources(textbooks, activity charts, etc.)
Platform:DIKSHA
Use:To deliver content
Printed books/ offline learning

Web portals & online resources
Mobile apps
DIKSHA
Saarthi Education
Madhi
Pratham
Madhi
iDream
ConveGenius
Moreover, for profit edtech solution enterprises such as Byju’s, Vedantu, Udemy, and Doubtnut made most of their content, including live tutorials, available for free once the pandemic struck,to further enable at-home learning for students.
Communication channels: Several states used the app to interact with students, parents and teachers, and establish communication groups between BRCs, CRCs, school heads, teachers and all stakeholders

Photo Source: Rocket Learning
Assessments: Used by stakeholders to conduct assessments and resolve doubts
Content delivery: Used by teachers and officials to deliver content to parents and students; by state officials to deliver content to teachers; and by other system officials for training
Feedback: Teachers used the app to interact with parents and elicit information on student performances
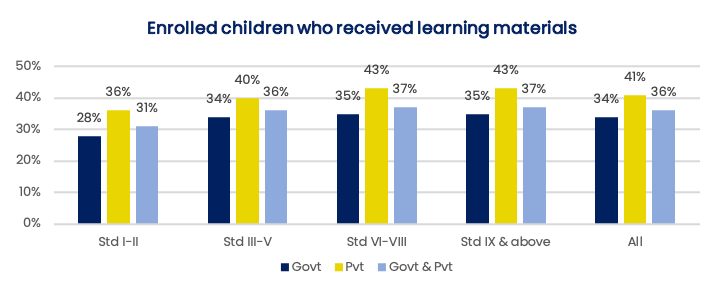
ASER1, which surveyed 52,227 rural households in September 2020, found that reach of at-home learning materials were limited in government as well as private schools:
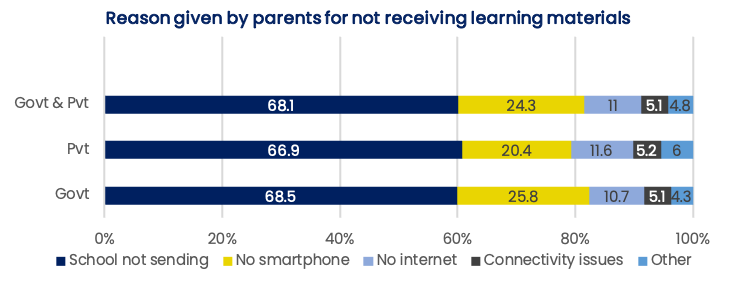
Delhi NCR Covid-19 Telephone Survey (NCAER, 2020)
The DCVTS Round 4 was conducted from 23 December 2020 and 4 January 2021 and interviewed 3,168 rural and urban households in
Delhi NCR
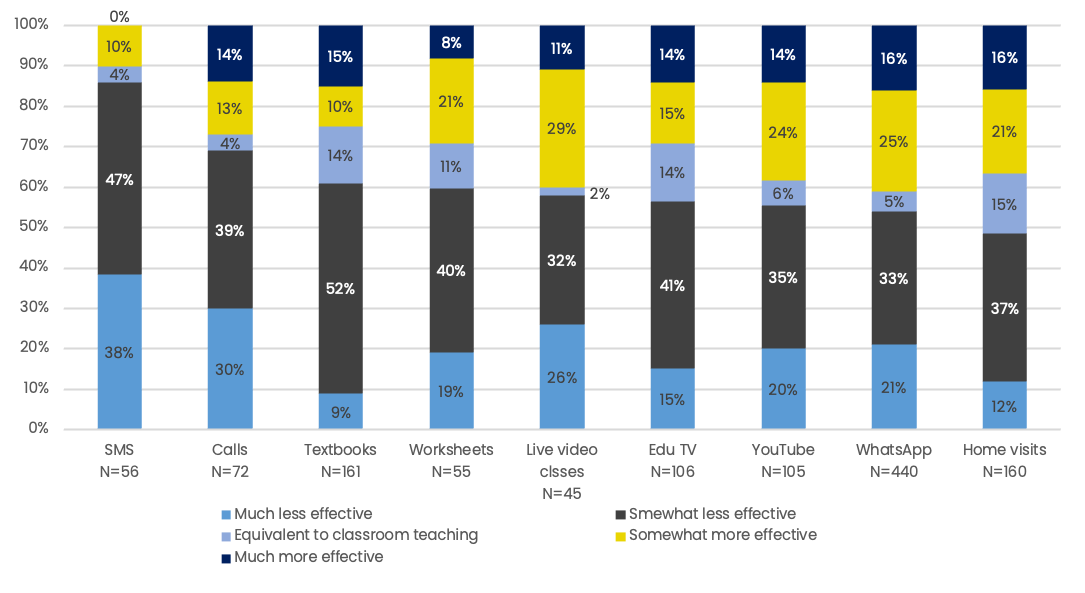
Tech-based tools for studying & learning
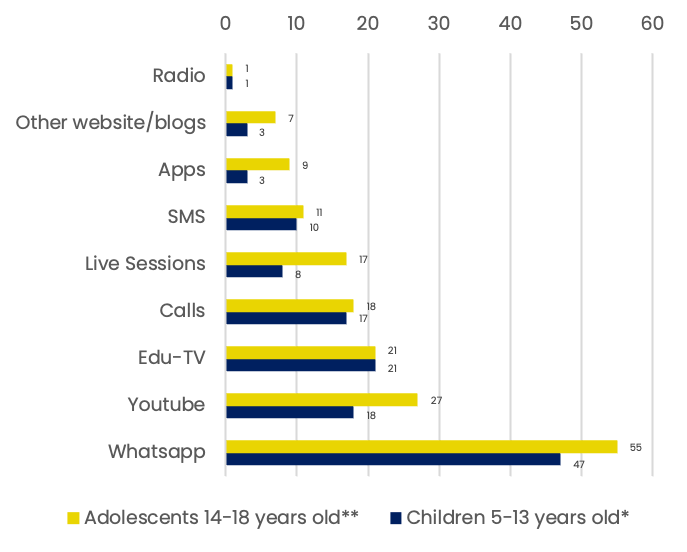
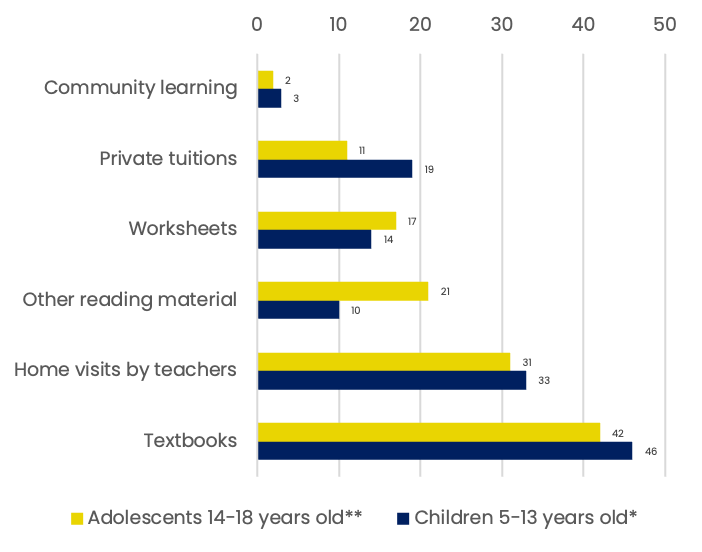
*n= 1862 **n= 1537
Traditional mediums for studying & learning
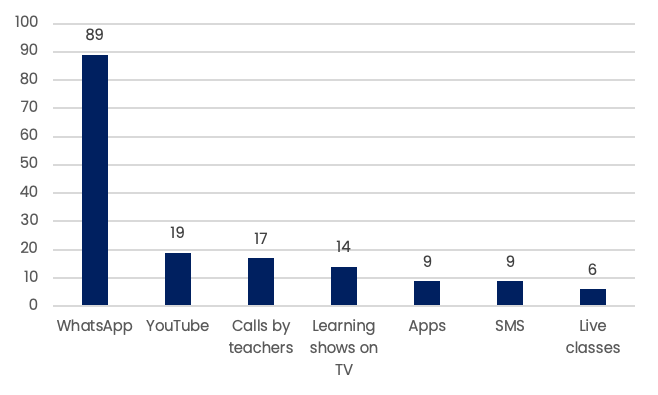
Technology based tools used for teaching
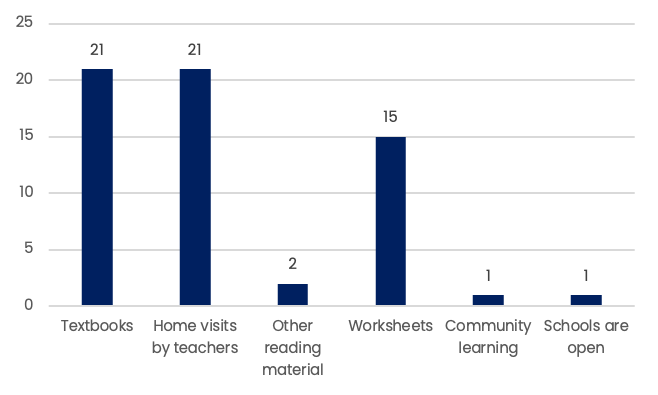
Traditional means used for teaching
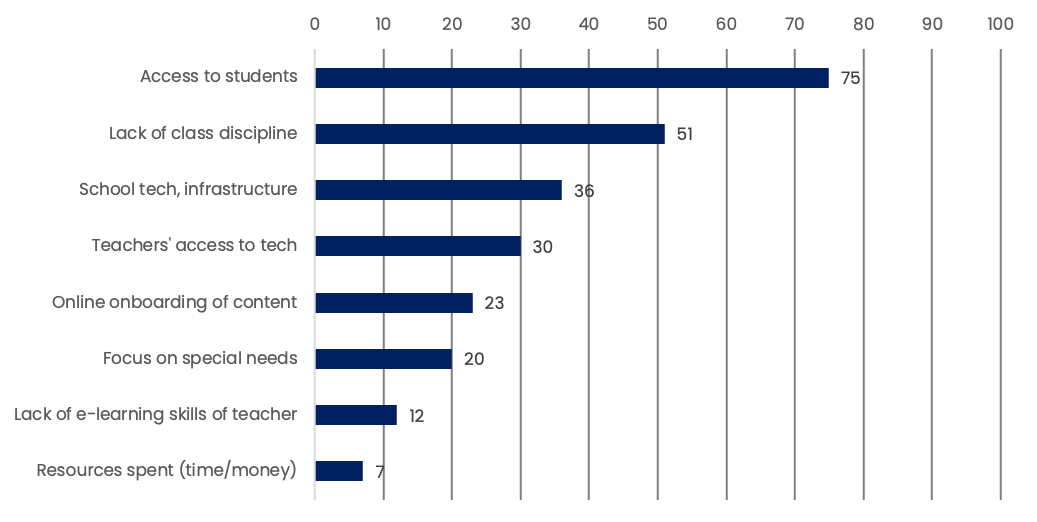
Challenges faced by teachers to conduct online classes
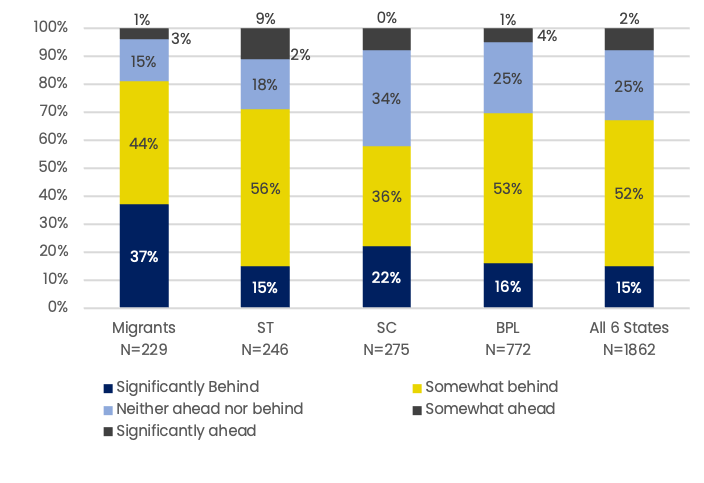
Parents’ perception of how children are learning now
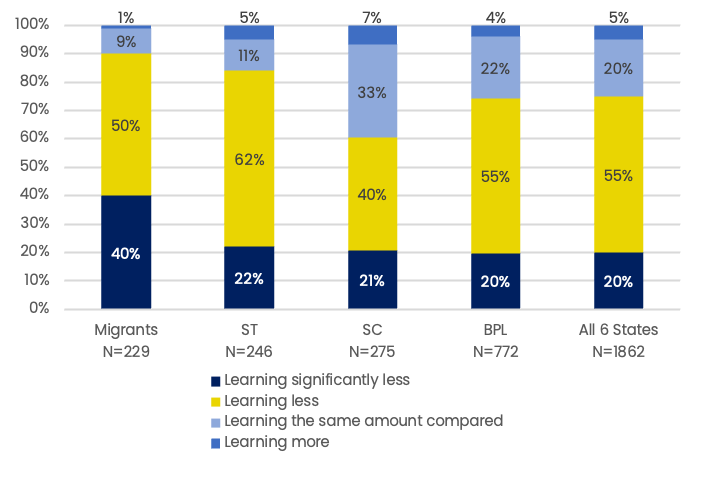
Perceptions of overall learning progress